The research trends and emerging hotspots in the lung cancer surgery literature in the recent decade have been characterized to inspire researchers with new targets and path-breaking directions for lung cancer research.
The article has been published in Health Data Science.
As lung cancer has remained the leading cause of global cancer death in the past years, thoracic surgery is acknowledged as the standard treatment for primary lung cancer, and global research enthusiasm keeps growing. However, the increasing number of publications related to lung cancer surgery makes it more and more difficult for researchers to keep up with the latest findings, even within the domain of their expertise.
Reporting the changing trends and hotspots of thoracic surgery research in lung cancer could potentially inspire researchers to identify new targeting research fields and path-breaking directions for research and generate evidence to support decision-making.
To better understand and follow the changing landscape of research on lung cancer surgery in the recent decade, this study utilized bibliometric and network analysis techniques to quantify the research trends and hotspots of lung cancer surgery. Using data from the Dimensions database, the research trends of scholarly output and scientific influence, cooperation networks, and emerging hotspots in lung cancer surgery research were analyzed.
“We aimed to provide researchers and policymakers with interesting insights into the changing research trends in lung cancer surgery and contribute to a better prognosis for patients with lung cancer,” says Dr. Jian Zhou at the Department of Thoracic Surgery, Peking University People’s Hospital.
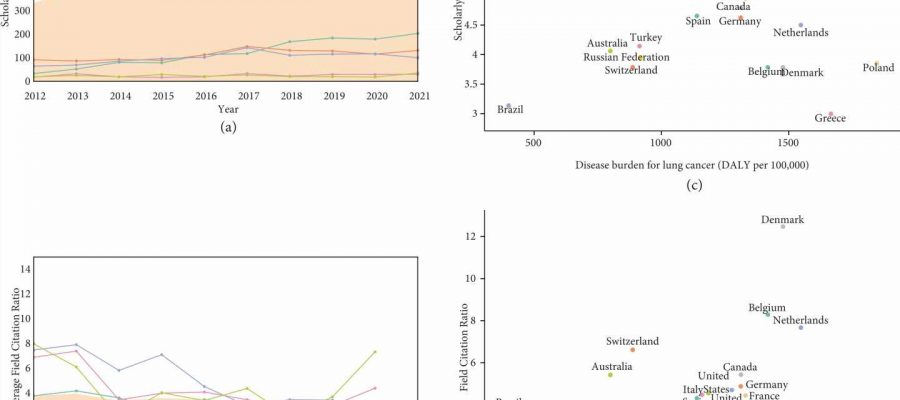
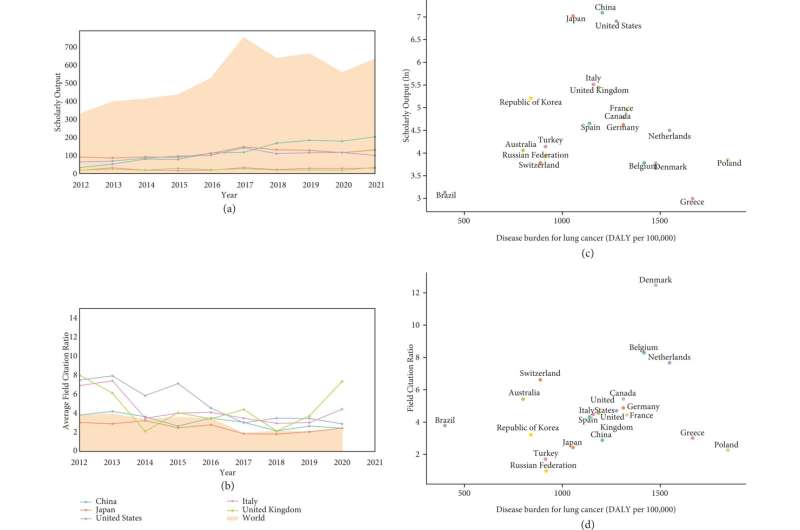
Establishing a global landscape of lung cancer surgery research in the recent decade, this study suggested growing participation across the world in lung cancer surgery research and an international cooperation research network dominated by the United States, China, and Europe.
However, collaboration in other Asian countries remained to be strengthened. Collaboration was more active between developed countries and more likely to produce high-quality outputs. In comparison, partnerships between other countries are less extended, which may suggest more efforts in supporting extensive global involvement in lung cancer research.
Significant variety was present in the scholarly outputs and scientific influence among different research areas in lung cancer surgery. Research in this field has been patient-centered, with specific interests in prevention, rehabilitation, and behavioral and social science. Immunotherapy has driven innovation in lung cancer surgery research and showcased promising influence in the recent decade, particularly regarding neoadjuvant immunotherapy, chemoimmunotherapy, and perioperative immunotherapy.
Take neoadjuvant immunotherapy as an example. Although current studies have preliminarily confirmed its role in improving the treatment’s effectiveness and safety, more studies are needed to investigate further its optimal use and health effect on patients with lung cancer.
Source: Read Full Article