Current guidelines used to plan salvage radiation treatments in patients with local recurrence of prostate cancer should be updated to take into consideration information derived from novel imaging modalities, such as PSMA PET, according to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2022 Annual Meeting. The study showed that PSMA PET was effective in identifying recurrences that fell partially or fully outside the clinical target volume as determined by current guidelines. This suggests that PSMA PET can be an invaluable tool for therapy planning.
After a biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer, salvage radiation therapy can be a curative approach. This therapy conducted following contouring guidelines based on expert consensus, such as the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) guidelines. In today’s era of precision medicine, study authors sought to determine if PSMA PET imaging could provide more detailed data on patterns of recurrence to inform therapy planning.
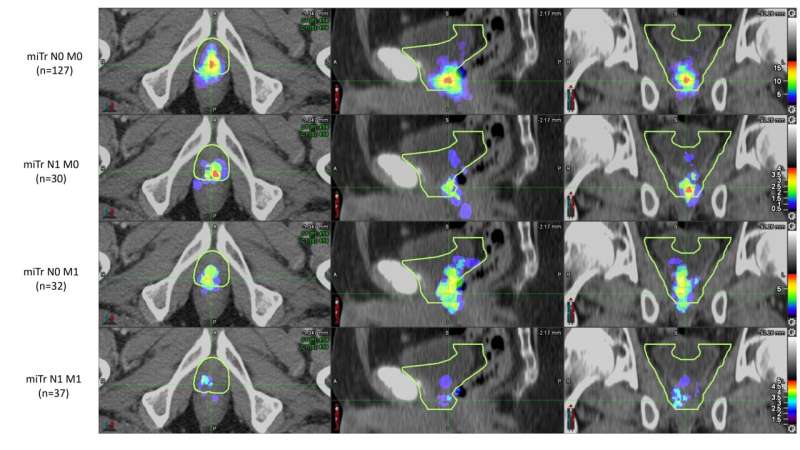
Prostate cancer patients who experienced biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy were included in the analysis if their PSMA PET/CT imaging showed recurrence in the prostate bed. To analyze the patterns of recurrence, two nuclear medicine physicians documented the areas of recurrence on the PSMA PET/CT, and four radiation oncologists (masked to the PSMA PET/CT findings) delineated the clinical target volume using RTOG guidelines on the CT images of the PET/CT. PSMA recurrence locations were then compared to the RTOG-based clinical target volumes.
PSMA recurrences were fully covered by the clinical target volumes in 54 percent of the patients. In 34 percent of the patients, PSMA recurrence was only partly covered, and in 13 percent of patients the PSMA recurrence was located fully outside of the clinical target volume.
Source: Read Full Article
